Choosing a work table in a laser plotter is, counter-intuitively, an important factor when selecting the parametersó of a cutting machine. Cutting on an improperly selected substrate can result in deterioration of the cutting edge, especially in the zone of the beam exit from the material, the formation of unwanted burns or even prevent the material from being cut completely. In addition, the correct choice of table helps to better dissipate the resulting smoke, dust and heat from under the material.
On the market, you will find many typesóof laser tablesódedicated to different typesóof clothes or materials. Below are coversót selected from them, used in low and medium power lasers (up to 250W).
PLASTER OF HONEY
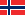
.One of the twoós most popular typesóof working tables in lasers. Honeycomb, because of its versatility, is a must-have for any plotter. It is great for applications requiring low reflexóness and optimal flatness. The small thickness of the single edge of the slice makes the reflections, although still visible, smaller than with tables of other types. In addition, with the use of an efficient extraction system, it can serve as a vacuum table, especially useful for cutting thin materialsów such as paper or leather.

Figure 1. Honeycomb workbench [1]
..
The undoubted disadvantage of honeycomb is the large number of small holesóin which dirt can collect, making it difficult to clean. Dirt on the surface of the table can result in the deterioration of the quality of the cutting edge or be transferred during the machiningóbce to the workpiece being made. An unquestionable advantage is the small size of the “mesh” of the mesh, thanks to which the cut details do not fall into the depths of the machine (which can happen when the workpiece has dimensions smaller than the knife spacing in the knife table).
Knife table
.

Figure 2. Knife workbench [1]
..
The second most common working table in laser plotters in use is the knife table. It consists of a dozen aluminum blades, the spacing and number of which can be adjusted. The ability to adjust the number of material support points to the sheet to be processed and the size of the finished parts allows us to maintain the correct focal length on the surface of the material with minimal contact with the table. The knife station is a great solution for cutting thicker materialós. In addition, the ability to adjust the spacing of the knives allows you to choose their distribution so that the cut shape is completely between one blade and the other. Thanks to this, no reflexes will be created on the cutting edge. On the other hand, workpieces with dimensions smaller than the knife spacing will fall into the machine. This type of work table is practically not used for working with thin and flaccid materials such as textiles or leatheróra. Materials with low rigidity will bend in the spaces between the knife blades, which can make it impossible to ensure the correct focal length across the material.
PINSTÓPINBAR
When defending delicate materialsó that are easily burned (such as wood or acrylic), the pin table comes to our aid. Depending on the design, pin tables come in a fixed version, without the possibility of modifying the distribution of pinsóor in a modular form where the distribution of pinsócan be adapted to a specific detail. The correct selectionór of pin distributionów It allows you to completely eliminate beam reflexes and achieve a perfect cutting edge without defectsów or burns. However, the pin stó? requires more attention to the correct alignment of the material, especially for tablesó? with variable pinó? positions. Incorrect alignment of the material, or inaccurate installation of the pinów in the base, can lead to incomplete support of the sheet and, as a result, alignment at an angle that makes it difficult to match the focal length across it.

Figure 3. pin working table [3]
..
Pin workstool
.
The advantage of this type of workbenchóon laser plotters is its ability to attach the material being workedóon to its surface by means of the vacuum generated. This is particularly advantageous for machining materials that do not precisely adhere to the table surface, such as paper or various types of films. The use of vacuum table can not only improve the quality of cutting and engraving, but also increase the efficiency of the process by reducing the time required to fix the material in the laser. The downside of such a solution is the significant contact area between the material and the table plane.
 Figure 4. Vacuum table for laser plotterós [4]
Figure 4. Vacuum table for laser plotterós [4]
For this reason, the vacuum stationó? is of limited use when cutting delicate materialsó? with a high-powered beam. Bouncing the beam off the table surface can cause burns, and stopping the beam run right after piercing the material can result in deterioration of the plotterós performance. You should also pay attention to the possibility of melting the edges of the material during cutting (this may be a feature of the material or a matter of improperly selected operating parameters), which can result in sticking of the workpiece to the surface of the table.
The cutter can also cause burns.
FERROMAGNETIC STÓŁ
.
The ferromagnetic stó? is a very simple element in its conception. It is a flat, smooth sheet with ferromagnetic properties. However, due to its very tight tolerances for flatness and surface roughness, it is a high-end component in laser plotters. The maximum smooth and flat surface ensures optimal engraving and cutting results for even the thinnestómaterials. And the completely ferromagnetic surface reduces the time it takes to mount the material in the working field by attaching it with magnetsów. However, due to the full contact of the material with the substrate, this tableós not recommended for cutting thicker and easily burnable materialsóat higher laser beam power settings. As with the vacuum table, you should payóattention to the possibility of over-melting the material and sticking to the table surface.
ACRYL TABLES
.
In addition to honeycomb and knife tables made of steel or aluminum, we can also find acrylic versions. Changing the material of which the table surface in contact with the workpiece is made allows, among other things, to reduce the weight of the table. At the same time, transparent acrylic almost completely does not reflect the laser beam, which makes it possible to completely eliminate the reflectionsóve produced during cutting, and thus to obtain an edge free from even the slightest burns. The price for increased cutting quality, however, is a reduction in the strength and durability of the working table. Placing too much weight on the surface of the table can lead to its breakage, and cutting with too much power at too low a speed carries the risk of cutting through the substrates.
The decision to choose the right workbench for the job is ultimately a product of many factorsón, including the type and thickness of the material and the power of the beam. However, with a properly selected substrate, we can achieve better cutting and engraving quality in laser plotters. Due to their versatility, the most popular are honeycomb – tables for engraving and cutting thin materialsóand knife – tables for cutting materialsóof greater thickness. In addition, in devices with a large working area, a pin stó?? is often found in a version with a fixed tooth distributionó??.
| . | .
reflexes . |
edge quality . |
universality . |
stability of material . |
mass . |
durability . |
| honeycomb | .||||||
| Knife stand | .||||||
| Stópin head | .||||||
| Vacuum stand | .||||||
| Ferromagnetic steel | .||||||
| Acrylic tables | .
Resources:
[1] https://atmsolutions.pl/
[2] https://www.cnc.info.pl/
[3] https://www.cnc.info.pl/pics/962fd6bdcace.jpg
[4] http://pl.haxcorematerial.com/vacuum-table/vacuum-table-for-printer/laser-cutter-vacuum-table.html